Nanotechnology: Commitment to sustainable development goals
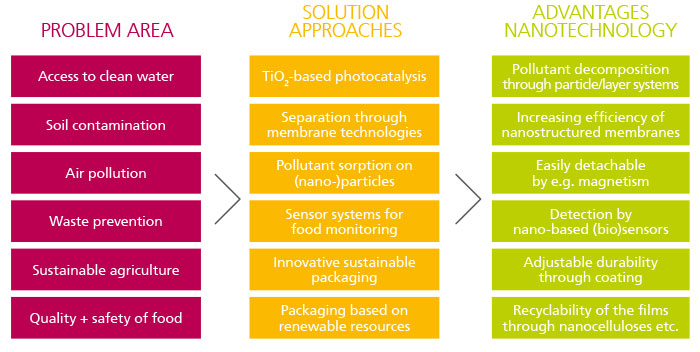
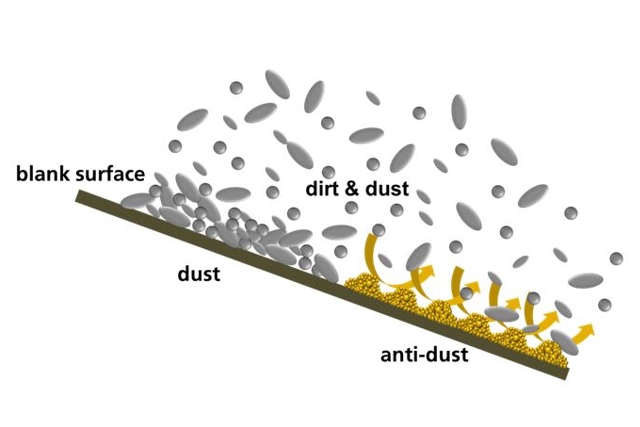
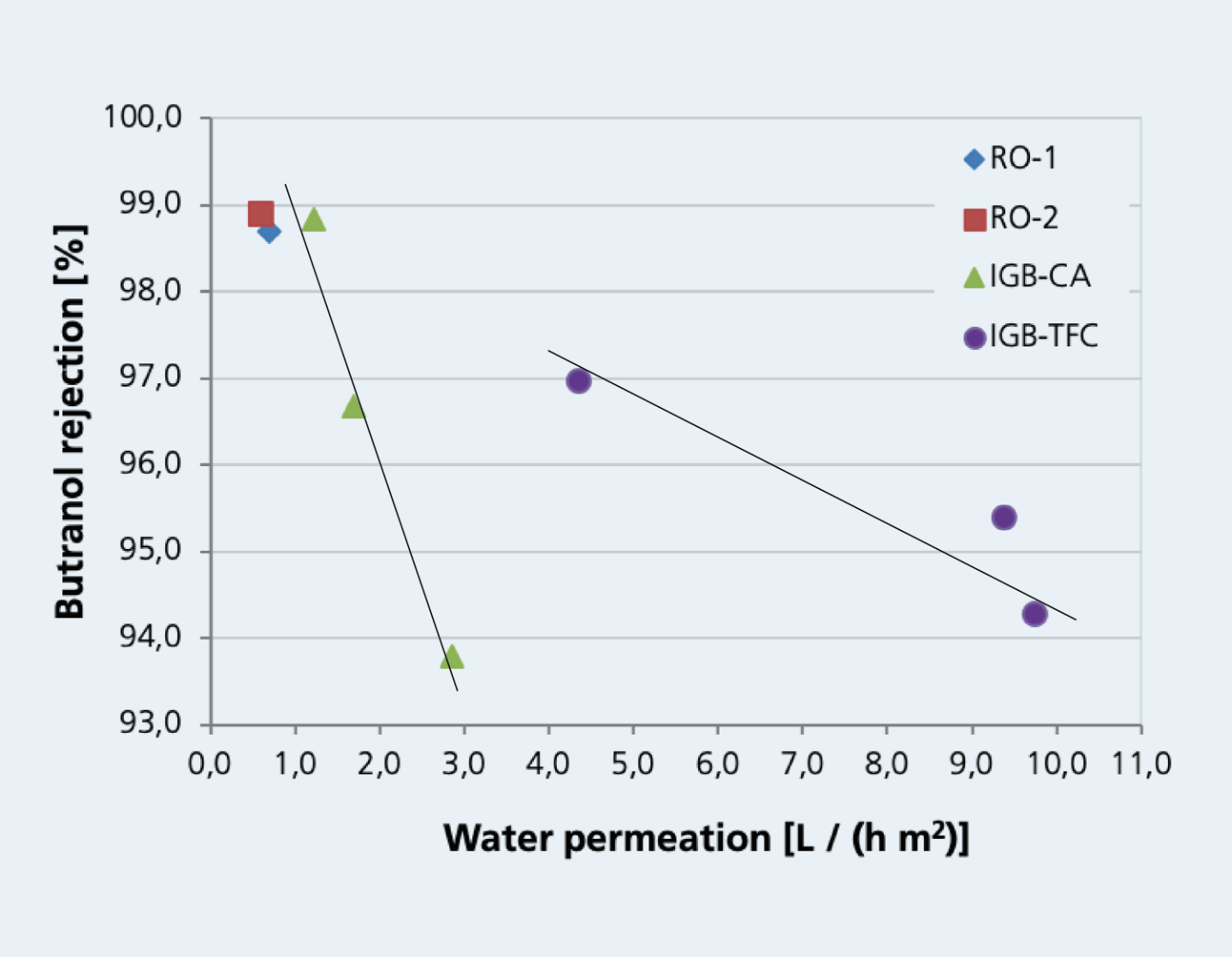
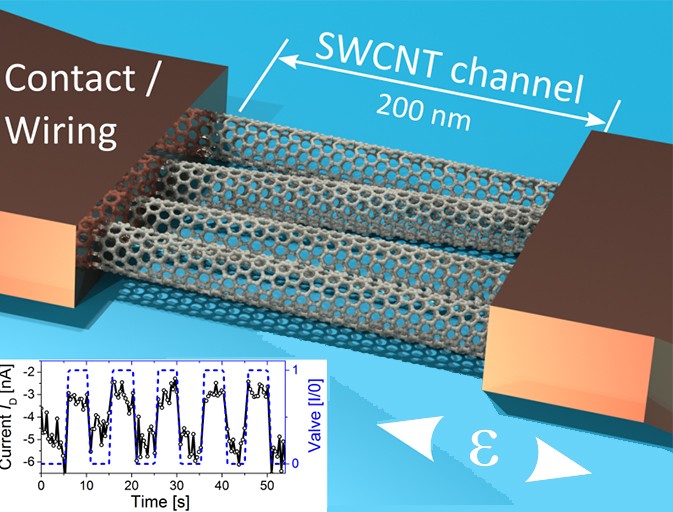
Nanotechnology is an interdisciplinary field of research that deals with the manipulation of matter at the atomic and molecular level. It offers enormous potential for tackling numerous global challenges and achieving the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Through the targeted control of materials at the nanoscale level, innovative solutions can be developed in areas such as energy, environmental protection, health, food security and water resources. For instance, nanotechnology can enhance resource efficiency, advance clean energy technologies, encourage environmentally friendly agricultural practices, and facilitate novel approaches to treating diseases. Nevertheless, it is crucial to ensure responsible development and use of nanotechnology to mitigate potential risks to humans and the environment.